Infertility: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment

Infertility: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Infertility is a common concern for couples who are trying to conceive, affecting millions of people worldwide. Understanding the underlying causes, recognizing the symptoms, seeking proper diagnosis, and exploring available treatments are key steps in addressing infertility
1. Causes of Infertility
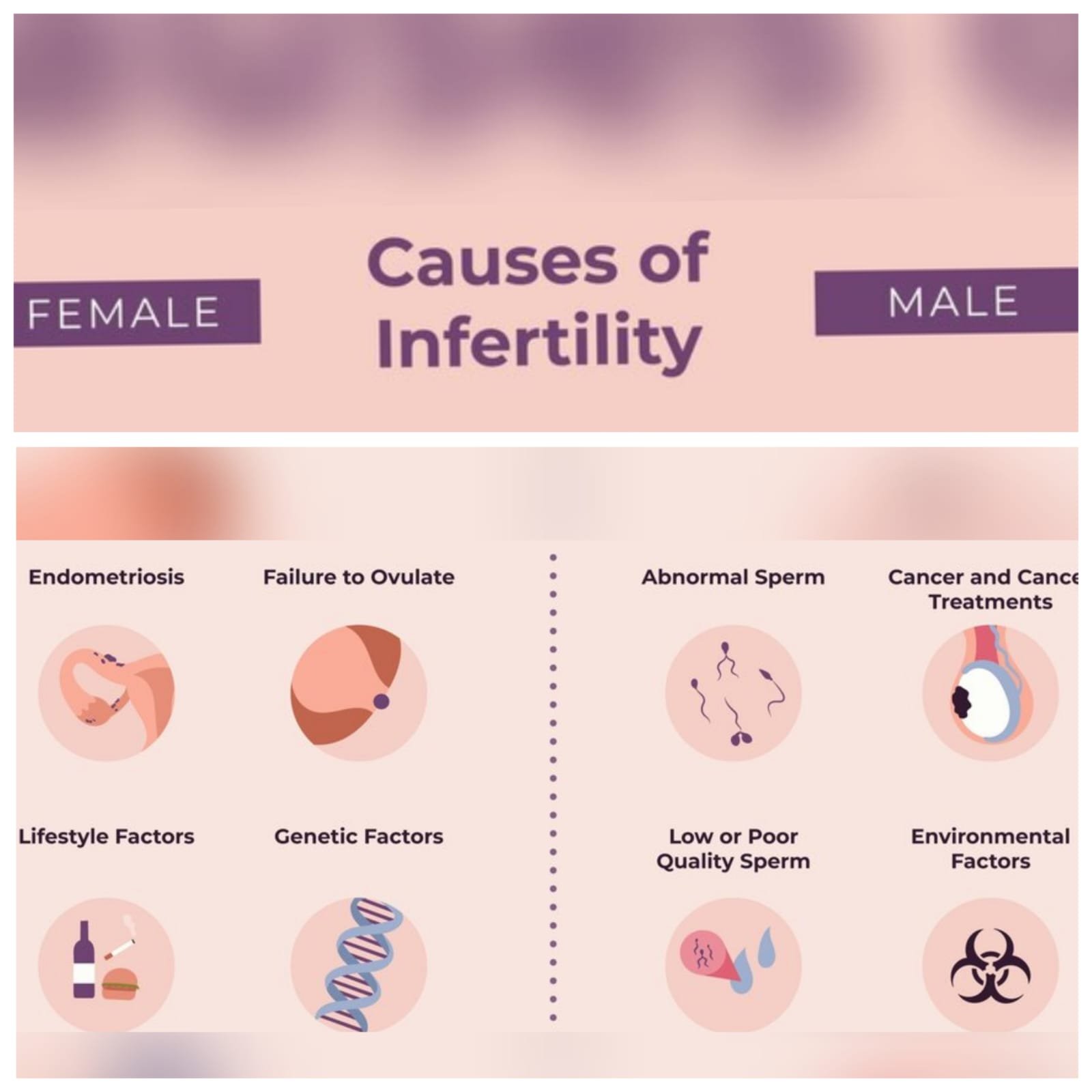
Infertility can affect both men and women, with various factors contributing to the inability to conceive. It is generally classified into male infertility, female infertility, or a combination of both.
Female Infertility Causes:
- Ovulation Disorders: Problems with ovulation account for nearly 25% of infertility cases. Conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, or premature ovarian failure (early menopause) can affect ovulation.
- Fallopian Tube Damage or Blockage: This may result from pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), endometriosis, or previous surgeries that cause scarring, preventing the sperm from reaching the egg.
- Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus grows outside it, affecting the function of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus.
- Uterine or Cervical Problems: Structural issues like uterine fibroids, polyps, or cervical stenosis (narrowing of the cervix) can block the path of the sperm or embryo.
- Age-related Decline: Fertility decreases with age, especially after age 35. Women are born with a finite number of eggs, and the quality of eggs declines with age, making conception more difficult.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions where the body’s immune system attacks reproductive organs, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, can impact fertility.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Problems with hormones responsible for the reproductive process, like FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone) or LH (Luteinizing Hormone), can lead to irregular menstrual cycles and hinder pregnancy.
Male Infertility Causes:
- Sperm Disorders: Poor sperm production, abnormal sperm shape (morphology), low sperm count, or slow-moving sperm (motility) are common causes of male infertility.
- Varicocele: A condition where the veins in the testicles are enlarged, affecting sperm production and quality.
- Infections: Infections like sexually transmitted infections (STIs), mumps, or inflammation of the testicles (orchitis) can impair sperm health.
- Ejaculation Issues: Retrograde ejaculation, where semen enters the bladder instead of exiting through the penis, or blocked ejaculation ducts can prevent sperm from reaching the egg.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Problems with hormones like testosterone or disorders of the pituitary gland can disrupt sperm production.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, stress, exposure to toxins (pesticides, heavy metals), and drug use can negatively impact fertility in men.
Combined or Unexplained Infertility:
In some cases, infertility may be caused by a combination of male and female factors, or the cause may remain unexplained despite thorough medical testing. Unexplained infertility can be frustrating, but it is still possible to pursue treatments.
2. Symptoms of Infertility
The primary symptom of infertility is the inability to conceive after one year of regular, unprotected intercourse. Other symptoms may vary depending on the underlying cause:
Female Symptoms:
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Infrequent or absent periods (amenorrhea) can indicate ovulation problems.
- Painful Periods: Severe cramps or pelvic pain may point to endometriosis or other reproductive disorders.
- Unusual Vaginal Discharge or Bleeding: Abnormal bleeding between periods or discharge may be a sign of infection or other reproductive health issues.
- Hormonal Changes: Symptoms like weight gain, acne, thinning hair, or excess facial hair could indicate conditions like PCOS or thyroid problems.
- Pelvic Pain: Chronic pain in the pelvic region can signal conditions like fibroids or endometriosis.
Male Symptoms:
- Changes in Sexual Function: Issues like difficulty ejaculating, reduced sexual desire, or erectile dysfunction can signal fertility problems.
- Testicular Pain or Swelling: Pain or lumps in the testicles may indicate infections, injury, or varicocele.
- Decreased Facial or Body Hair: Hormonal imbalances may result in reduced hair growth.
- Small, Firm Testicles: Structural problems like varicocele or hormonal issues can affect testicle size and sperm production.
3. Diagnosis of Infertility
Diagnosing infertility involves a series of tests and evaluations to pinpoint the underlying cause. Both partners are usually tested to understand the fertility challenges.
For Women:
- Ovulation Testing: Blood tests to measure hormone levels, such as luteinizing hormone (LH) and progesterone, are used to confirm whether ovulation is occurring.
- Hysterosalpingography (HSG): An X-ray procedure to check the fallopian tubes and uterus for blockages or abnormalities.
- Pelvic Ultrasound or Laparoscopy: Used to detect structural issues like fibroids, polyps, or endometriosis.
- Ovarian Reserve Testing: Blood tests and ultrasounds that evaluate the quality and quantity of eggs remaining in the ovaries.
- Genetic Testing: Helps identify genetic disorders that may impact fertility.
For Men:
- Semen Analysis: The most common fertility test for men, evaluating the quantity, shape, and movement of sperm.
- Hormonal Testing: Blood tests that measure levels of testosterone and other hormones affecting sperm production.
- Scrotal Ultrasound: Helps detect issues like varicocele or blockages in the ducts.
- Genetic Testing: Identifies any chromosomal abnormalities that might be causing infertility.
- Testicular Biopsy: In rare cases, a biopsy may be done to assess sperm production.

4. Treatment of Infertility
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may involve medical intervention, lifestyle changes, or assisted reproductive technologies (ART). The goal is to either restore fertility or improve the chances of conception.
For Women:
- Fertility Medications: Drugs like Clomiphene citrate (Clomid) or Letrozole are often prescribed to stimulate ovulation. Hormonal medications may also be used to regulate or induce ovulation.
- Surgery: Laparoscopic surgery may be used to treat structural problems like endometriosis, fibroids, or fallopian tube blockages.
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): In IUI, sperm is directly inserted into the uterus around the time of ovulation, increasing the chances of fertilization.
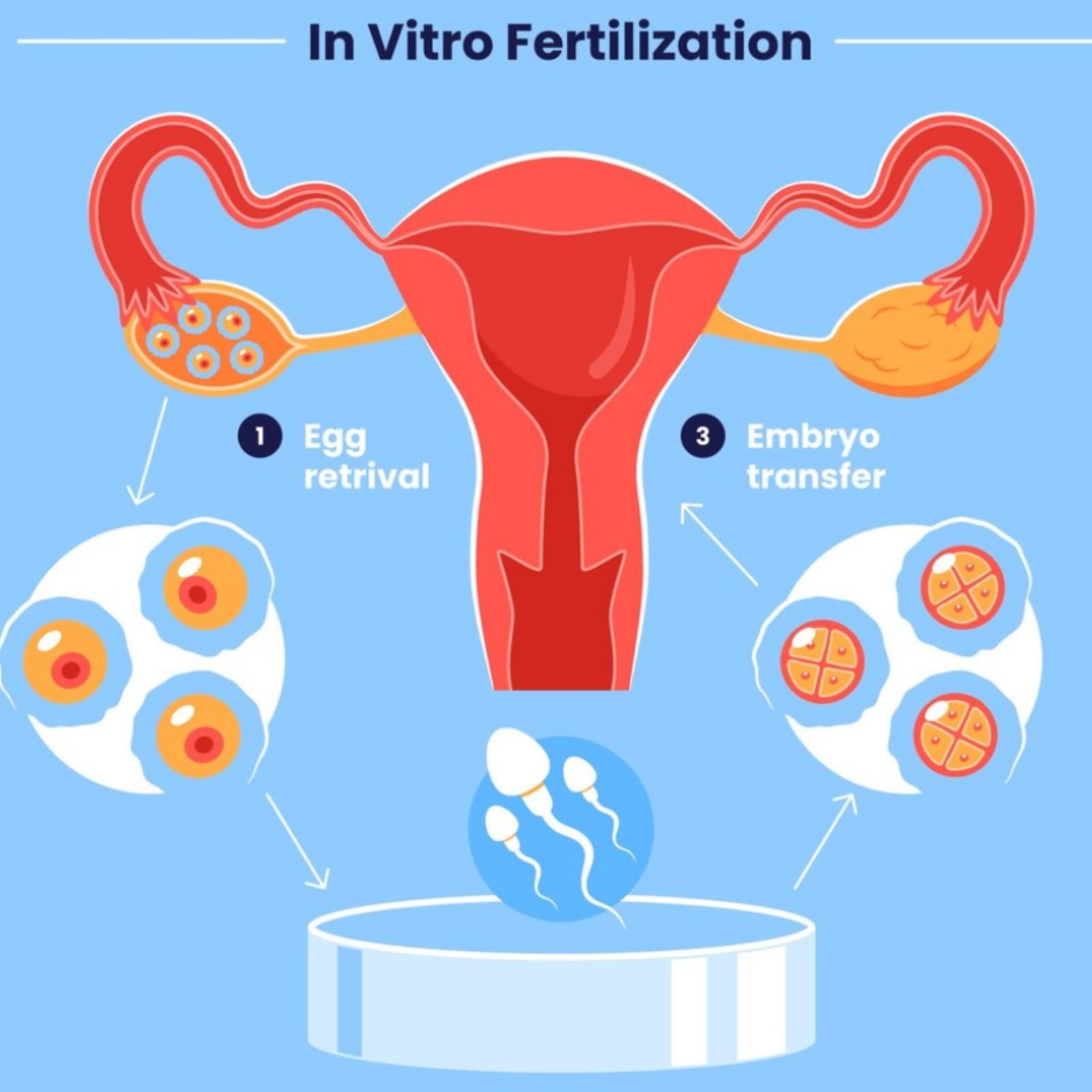
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): IVF is a process in which eggs are retrieved, fertilized with sperm in a lab, and the resulting embryo is transferred to the uterus. It’s one of the most effective treatments for various fertility issues.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, avoiding tobacco and alcohol, and ensuring a balanced diet can improve fertility.
For Men:
- Fertility Medications: Hormonal treatments like gonadotropins may be prescribed to improve sperm production.
- Surgery: Surgical interventions like varicocele repair or vasectomy reversal may improve sperm function. In cases of blockages, sperm can be retrieved surgically.
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): IUI can also be used for male infertility when sperm count or motility is low.
- Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART): Procedures like IVF or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI), where a single sperm is injected into an egg, may be recommended for severe male infertility.
- Lifestyle Changes: Improving diet, exercise, reducing stress, and avoiding harmful substances can significantly boost fertility.
Conclusion
Infertility is a multifaceted issue, often involving both male and female factors. However, with advances in medical technology and treatments, many couples have successfully overcome infertility challenges. Early diagnosis and intervention can greatly improve the chances of conception, whether through lifestyle changes, medications, or advanced reproductive technologies like IVF. For couples struggling with infertility, consulting with a fertility specialist can provide personalized guidance and support throughout the journey.